手动实现 Spring 底层机制
初始化IOC容器+依赖注入+BeanPostProcessor 机制+AOP
引入需要的jar 包
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.hspedu</groupId>
<artifactId>hsp-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.8</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>类加载器
| 类型 | |
|---|---|
| Bootstrap 类加载器 | 对应路径 jre/lib |
| Ext 类加载器 | 对应路径 jre/lib/ext |
| App 类加载器 | 对应路径 classpath |
● classpath 类路径,就是java.exe 执行时,指定的路径,比如
bash
D:\program\hspjdk8\bin\java.exe "-javaagent:D:\program\JavaIDEA
2020.2\lib\idea_rt.jar=55992:D:\program\JavaIDEA 2020.2\bin" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\charsets.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\deploy.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ ext\access-bridge-64.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\cldrdata.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\dnsns. jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\jaccess.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\jfxrt.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8 \jre\lib\ext\localedata.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\nashorn.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\sune
c.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\sunjce_provider.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\sunmscapi.jar;D:\ program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\sunpkcs11.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\ext\zipfs.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jr e\lib\javaws.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\jce.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\jfr.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jr e\lib\jfxswt.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\jsse.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\management-agent.jar;D:\p rogram\hspjdk8\jre\lib\plugin.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\resources.jar;D:\program\hspjdk8\jre\lib\rt.jar;D:\java_projects\hsp-myspring\target\classes com.hspedu.spring.AppMain获取方法注解的值
java
package com.hspedu.spring.component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.*;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 老师说明:SmartAnimalAspect当做一个切面类来使用
* ,后面老师再分析如何做的更加灵活
*/
@Aspect //我们的注解
@Component //这是实现了
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
@Before(value = "execution com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog getSum")
public static void showBeginLog() {
System.out.println("前置通知..");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog getSum")
public static void showSuccessLog() {
System.out.println("返回通知..");
}
}java
package com.hspedu.spring;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.AfterReturning;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Before;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.SmartAnimalAspect;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
public class HspTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
//1. 获取SmartAnimalAspect的class对象
Class<SmartAnimalAspect> smartAnimalAspectClass = SmartAnimalAspect.class;
//2. 遍历该类的所有方法
for (Method declaredMethod : smartAnimalAspectClass.getDeclaredMethods()) {
//如果切面类的方法有Before注解
if (declaredMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Before.class)) {
//得到切面类的切入方法名
System.out.println("m:= " + declaredMethod.getName());
//得到Before(value="xxxx")
//得到Before注解
Before annotation = declaredMethod.getAnnotation(Before.class);
//得到Before注解的value
System.out.println("value:= " + annotation.value());
//得到切入要执行的方法.[反射基础]
Method declaredMethod1 = smartAnimalAspectClass.getDeclaredMethod(declaredMethod.getName());
//调用切入方法[通过反射调用]
declaredMethod1.invoke(smartAnimalAspectClass.newInstance(), null);
} else if (declaredMethod.isAnnotationPresent(AfterReturning.class)) {
//如果发现切面类有AfterReturning注解,同样可以进行处理..
System.out.println("m:= " + declaredMethod.getName());
AfterReturning annotation = declaredMethod.getAnnotation(AfterReturning.class);
System.out.println("value:= " + annotation.value());
//得到切入要执行的方法.
Method declaredMethod1 = smartAnimalAspectClass.getDeclaredMethod(declaredMethod.getName());
//调用切入方法[反射调用]
declaredMethod1.invoke(smartAnimalAspectClass.newInstance(), null);
}
}
}
}Spring 整体架构分析
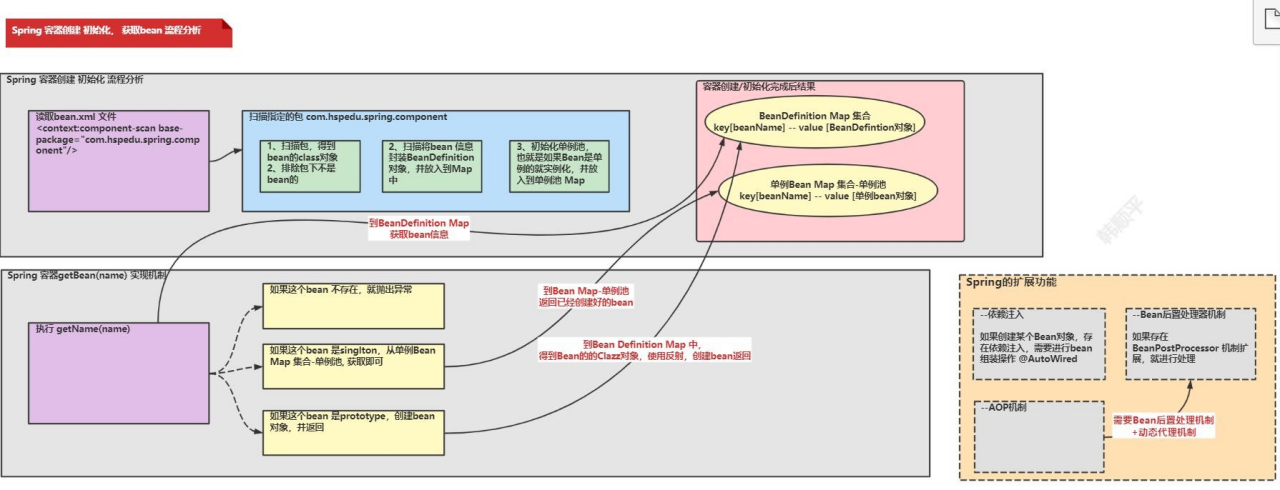
代码实现
| 实现步骤 |
|---|
| 阶段 1- 编写自己 Spring 容器,实现扫描包, 得到bean 的 class 对象 |
| 阶段 2- 扫描将 bean 信息封装到 BeanDefinition |
| 阶段 3- 初始化 bean 单例池,并完成 getBean 方法, createBean 方法 |
| 阶段 4- 完成依赖注入 |
| 阶段 5- bean 后置处理器实现 |
| 阶段 6- AOP 机制实现 |
在创建好 Bean 实例后,判断是否需要进行初始化【老师心得: 容器中常用的一个方法是,根据该类是否实现了某个接口,来判断是否要执行某个业务逻辑, 这里 韩顺平Java 工程师其实就是 java 基础的接口编程实际运用
java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 老韩解读
* 1. @Target(ElementType.TYPE)指定我们的ComponentScan注解可以修饰 Type程序元素
* 2. @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 指定ComponentScan注解 保留范围
* 3. String value() default ""; 表示ComponentScan 可以传入 value
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ComponentScan {
//通过value可以指定要扫描的包
String value() default "";
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 定义我们的 Component 注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
//通过value可以给注入的bean/对象指定名字
String value() default "";
}JAVA
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 这是一个配置类, 作用类似我们原生spring的 beans.xml 容器配置文件
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.hspedu.spring.component")
public class HspSpringConfig {
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* Scope 可以指定Bean的作用范围[singleton, prototype]
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Scope {
//通过value可以指定singleton,prototype
String value() default "";
}JAVA
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
//这里属性,同学可以参考老师的思路完成,还是比较简单
//boolean required() default true;
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface Aspect {
String value() default "";
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Before {
String value();
String argNames() default "";
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface After {
String value();
String argNames() default "";
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface AfterReturning {
String value() default "";
String pointcut() default "";
String returning() default "";
String argNames() default "";
}java
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 老师解读
* 1. 我们根据原生Spring 定义了一个InitializingBean
* 2. 该InitializingBean接口有一个方法void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
* 3. afterPropertiesSet() 在Bean的 setter后执行,即就是我们原来的初始化方法
* 4. 当一个Bean实现这个接口后,就实现afterPropertiesSet() , 这个方法就是初始化方法
*/
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}JAVA
package com.hspedu.spring.component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Scope;
import com.hspedu.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component(value = "monsterDao")
//@Scope(value = "prototype")
public class MonsterDao implements InitializingBean {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("MonsterDao-hi()");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MonsterDao 初始化方法被调用...");
}
}java
package com.hspedu.spring.component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.hspedu.spring.processor.BeanPostProcessor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 说明
* 1. 这是我们自己的一个后置处理器
* 2. 实现了BeanPostProcessor
* 3. 我们可以重写before和after方法
* 4. 在Spring容器中,仍然把HspBeanPostProcessor当做一个Bean对象, 要在注入到容器
* 5. @Component 标识
* 6. 我们要让HspBeanPostProcessor成为真正的后置处理器, 需要在容器中加入业务代码
* 7. 还要考虑多个后置处理器对象注入到容器问题
*/
@Component
public class HspBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
//这里请小伙伴一定要体会到,后置处理器是会容器的创建的bean生效
//,相当于是可以对多个对象编程, 切面编程
//日志,权限,身份, 事务.......
if (bean instanceof Car) {
System.out.println("这是一个Car对象, 我可以处理");
//((Car)bean)
}
System.out.println("后置处理器HspBeanPostProcessor Before调用 bean类型="
+ bean.getClass() + " bean的名字=" + beanName);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println("后置处理器HspBeanPostProcessor After调用 bean类型="
+ bean.getClass() + " bean的名字=" + beanName);
//实现AOP, 返回代理对象, 即对Bean进行包装
//1. 先死后活-> 后面我们可以通过注解就可以更加灵活
if ("smartDog".equals(beanName)) {
//使用Jdk的动态代理,返回返回bean的代理对象
//如果没有印象的小伙伴,回去看老韩讲过的动态代理
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(HspBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(),
bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("method=" + method.getName());
Object result = null;
//假如我们进行前置通知+返回通知 处理的方法是getSum
//后面可以通过注解来做的更加灵活
if ("getSum".equals(method.getName())) {
SmartAnimalAspect.showBeginLog();
result = method.invoke(bean, args);//执行目标方法
//进行返回通知的处理
SmartAnimalAspect.showSuccessLog();
} else {
result = method.invoke(bean, args);//执行目标方法
}
return result;
}
});
//如果bean是需要返回代理对象的, 这里就直接return proxyInstance
return proxyInstance;
}
//如果不需要AOP, 返回 bean
return bean;
}
}JAVA
package com.hspedu.spring.component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Autowired;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Scope;
import com.hspedu.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 说明MonsterService 是一个Service
* 1. 如果指定了value,那么在注入spring容器时,以你指定为准
* 2. 如果没有指定value ,则使用类名首字母小写名字
*/
@Component//(value = "monsterService") //把MonsterService注入我们自己的spring容器中
@Scope(value = "prototype")
public class MonsterService implements InitializingBean {
//这里我们使用自己的@Autowired来修饰属性
//表示该属性,是通过容器完成依赖注入
//说明: 我们实现按照名字来进行组装即可
@Autowired
private MonsterDao monsterDao;
public void m1() {
monsterDao.hi();
}
/**
* 老师解读
* 1. afterPropertiesSet就是在bean的setter方法执行完毕后被spring容器调用
* 2 即就是初始化方法
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("MonsterService 初始化方法被调用 程序员在这里加入初始化的业务..");
}
}JAVA
package com.hspedu.spring.ioc;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* BeanDefinition 用于封装/记录Bean的信息[1. scope 2 Bean对应的Class对象, 反射可以生对应的对象]
*/
public class BeanDefinition {
private String scope;
private Class clazz;
//可以根据需求,进行扩展
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public Class getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BeanDefinition{" +
"scope='" + scope + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
}java
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 老师说明:SmartAnimalAspect当做一个切面类来使用
* ,后面老师再分析如何做的更加灵活
*/
@Aspect //我们的注解
@Component //这是实现了
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
@Before(value = "execution com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog getSum")
public static void showBeginLog() {
System.out.println("前置通知..");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "execution com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog getSum")
public static void showSuccessLog() {
System.out.println("返回通知..");
}
}JAVA
package com.hspedu.spring.ioc;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Autowired;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Component;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.ComponentScan;
import com.hspedu.spring.annotation.Scope;
import com.hspedu.spring.processor.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.hspedu.spring.processor.InitializingBean;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* HspSpringApplicationContext 类的作用类似Spring原生ioc容器
*/
public class HspSpringApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
//定义属性BeanDefinitionMap -> 存放BeanDefinition对象
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//定义属性SingletonObjects -> 存放单例对象
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> singletonObjects =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//定义一个属性beanPostProcessorList, => 存放后置处理器
private List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessorList =
new ArrayList<>();
//构造器
public HspSpringApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
//完成扫描指定包
beanDefinitionsByScan(configClass);
//通过beanDefinitionMap , 初始化singletonObjects 单例池
//封装成方法
//遍历所有的beanDefinition对象
//这里是java基础->集合和枚举
Enumeration<String> keys = beanDefinitionMap.keys();
while (keys.hasMoreElements()) {
//得到beanName
String beanName = keys.nextElement();
//通过beanName 得到对应的beanDefinition对象
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
//判断该bean是singleton还是prototype
if ("singleton".equalsIgnoreCase(beanDefinition.getScope())) {
//将该bean实例放入到singletonObjects 集合
Object bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
singletonObjects.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
//System.out.println("singletonObjects 单例池=" + singletonObjects);
//System.out.println("beanDefinitionMap=" + beanDefinitionMap);
}
//该方法完成对指定包的扫描,并将Bean信息封装到BeanDefinition对象,在放入到Map
public void beanDefinitionsByScan(Class configClass) {
this.configClass = configClass;
//获取要扫描的包
//1. 先得到HspSpringConfig配置的的@ComponentScan(value = "com.hspedu.spring.component")
ComponentScan componentScan =
(ComponentScan) this.configClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2. 通过componentScan的value=> 即要扫描的包
String path = componentScan.value();
System.out.println("要扫描的包= " + path);
//得到要扫描的包下的所有资源(类 .class)
//1.得到类的加载器->APP 类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader =
HspSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//2. 通过类的加载器获取到要扫描的包的资源 url=》类似一个路径
path = path.replace(".", "/");//一定要把. 替换成 /
URL resource =
classLoader.getResource(path);
System.out.println("resource=" + resource);
//3. 将要加载的资源(.class) 路径下的文件进行遍历=>io
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//System.out.println("=====================");
//System.out.println("=" + f.getAbsolutePath());
String fileAbsolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
//这里我们只处理.class文件
if (fileAbsolutePath.endsWith(".class")) {
//1. 获取到类名
String className =
fileAbsolutePath.substring(fileAbsolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, fileAbsolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//2. 获取类的完整的路径(全类名)
//老师解读 path.replace("/",".") => com.hspedu.spring.component.
String classFullName = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
//3. 判断该类是不是需要注入容器, 就看该类是不是有注解 @Component @Service..
try {
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
//如果该类使用了@Component, 说明是Spring bean
System.out.println("是一个Spring bean =" + clazz + " 类名=" + className);
//老师说明
//1. 为了方便,老韩这里将后置处理器放入到一个ArrayList
//2. 如果发现是一个后置处理器, 放入到 beanPostProcessorList
//3. 在原生的Spring容器中, 对后置处理器还是走的getBean, createBean
// , 但是需要我们在singletonObjects 加入相应的业务逻辑
//4. 因为这里我们是为了讲解后置处理去的机制,我就简化
//5. 如果小伙伴们,仍然走以前的逻辑,也可以,就是要麻烦一点
//判断当前的这个clazz有没有实现BeanPostProcessor
//说明, 这里我们不能使用 instanceof 来判断clazz是否实现了BeanPostProcessor
//原因: clazz不是一个实例对象,而是一个类对象/clazz, 使用isAssignableFrom
//小伙伴将其当做一个语法理解
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor =
(BeanPostProcessor) clazz.newInstance();
//放入到beanPostProcessorList
beanPostProcessorList.add(beanPostProcessor);
continue;
}
//先得到beanName
//1. 得到Component注解
Component componentAnnotation =
clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Component.class);
//2. 的配置value值, 疑问 如果程序员没有配置value[后面处理..]
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
if ("".equals(beanName)) {//如果没有写value
//将该类的类名首字母小写作为beanName
beanName = StringUtils.uncapitalize(className);
}
//3.将Bean的信息封装到BeanDefinition对象->放入到BeanDefinitionMap
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClazz(clazz);
//4. 获取Scope值
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
//如果配置了Scope, 获取他配置的值
Scope scopeAnnotation = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(Scope.class);
beanDefinition.setScope(scopeAnnotation.value());
} else {
//如果没有配置Scope, 就默认的值singleton
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
//蒋beanDefinition 对象放入到Map
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
} else {
//如果该类没有使用了@Component, 说明不是Spring bean
System.out.println("不是一个Spring bean =" + clazz + " 类名=" + className);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("===============================");
}
}
}
//完成createBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) 方法
//老师说明,目前,我们先简单实现
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//得到Bean的clazz对象
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getClazz();
try {
//使用反射得到实例
Object instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
//老师分析: 这里老韩会加入依赖注入的业务逻辑!!!
//1. 遍历当前要创建的对象的所有字段
for (Field declaredField : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
//2. 判断这个字段是否有@Autowired
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
//提示一下
//处理@Autowired 的required ,很简单
//Autowired annotation = declaredField.getAnnotation(Autowired.class)
//annotation.required()=> 然后根据true, 是false 进行其它处理..
//3. 得到这个字段名字
String name = declaredField.getName();
//4. 通过getBean方法来获取要组装对象
Object bean = getBean(name);
//5. 进行组装
declaredField.setAccessible(true);//因为属性是pirvate, 需要暴破
declaredField.set(instance, bean);
}
}
System.out.println("=====创建好实例====" + instance);
//我们在Bean的初始化方法前,调用后置处理器的before方法
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
//在后置处理器的before方法,可以对容器的bean实例进行处理
//然后返回处理后的bean实例, 相当于做一个前置处理
Object current =
beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance, beanName);
if (current != null) {
instance = current;
}
}
//这里判断是否要执行Bean初始化方法
//1. 判断当前创建的Bean对象是否实现了InitializingBean
//2. instanceof java基础中讲 表判断某个对象的运行类型是不是某个类型或者
// 某个类型的子类型
//3. 这里就使用到接口编程
if (instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
//3.将instance转成InitializingBean类型
try {
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//我们在Bean的初始化方法后,调用后置处理器的after方法
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
//在后置处理器的after方法,可以对容器的bean实例进行处理
//然后返回处理后的bean实例, 相当于做一个后置处理
//原生Spring容器,比我们这个还要复杂
Object current =
beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
if(current != null) {
instance = current;
}
}
System.out.println("------------------------------");
return instance;
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//如何反射创建对象失败
return null;
}
//编写方法getBean(String name),编写方法返回对容器中对象
public Object getBean(String name) {
//老师加一个判断,传入的beanName是否在beanDefinitionMap中存在..
if (beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(name)) {//如果存在
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(name);
//得到beanDefinition的scope, 分别进行处理
if ("singleton".equalsIgnoreCase(beanDefinition.getScope())) {
//说明是单例配置, 就直接从单例池获取
return singletonObjects.get(name);
} else {//如果不是单例的,我就调用createBean, 反射一个对象
return createBean(name, beanDefinition);
}
} else {//如果不存在
//抛出一个空指针异常-小伙伴也可以自定义-Java基础异常
throw new NullPointerException("没有该bean");
}
}
} Blog
Blog