AOP
官方文档
AOP 讲解: spring-framework-5.3.8/docs/reference/html/core.html#aop
AOP APIs : spring-framework-5.3.8/docs/reference/html/core.html#aop-api
动态代理-精致小案例
需求说明
- 有 Vehicle(交通工具接口, 有一个 run 方法), 下面有两个实现类Car 和Ship
- 当运行 Car 对象 的 run 方法和 Ship 对象的 run 方法时,输入如下内容, 注意观察前后有统一的输出
交通工具开始运行了...
大轮船在水上 running...
交通工具停止运行了...交通工具开始运行了...
小汽车在公路上 running...
交通工具停止运行了...传统方案
传统的解决思路,在各个方法的[前,执行过程, 后]输出日志提示信息
public interface Vehicle {
public void run();
public String fly(int height);
}public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了....");
System.out.println("小汽车在路上 running....");
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了....");
}
@Override
public String fly(int height) {
System.out.println("小汽车可以飞翔 高度=" + height);
return "小汽车可以飞翔 高度=" + height;
}
}public class Ship implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了....");
System.out.println("大轮船在水上 running....");
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了....");
}
@Override
public String fly(int height) {
System.out.println("轮船可以飞翔 高度=" + height);
return "轮船可以飞翔 高度=" + height;
}
}@Test
public void run() {
//OOP基础=>java基础
Vehicle vehicle = new Ship();
//动态绑定
vehicle.run();
}动态代理
动态代理解决思路,在调用方法时,使用反射机制,根据方法去决定调用哪个对象方法
public interface Vehicle {
public void run();
public String fly(int height);
}public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("小汽车在路上 running....");
}
@Override
public String fly(int height) {
System.out.println("小汽车可以飞翔 高度=" + height);
return "小汽车可以飞翔 高度=" + height;
}
}public class VehicleProxyProvider {
//定义一个属性
//target_vehicle 表示真正要执行的对象
//该对象实现了Vehicle接口
private Vehicle target_vehicle;
//构造器
public VehicleProxyProvider(Vehicle target_vehicle) {
this.target_vehicle = target_vehicle;
}
//编写一个方法,可以返回一个代理对象, 该代理对象可以通过反射机制调用到被代理对象的方法
//老师解读
//1. 这个方法非常重要, 理解有一定难度
public Vehicle getProxy() {
//得到类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader =
target_vehicle.getClass().getClassLoader();
//得到要代理的对象/被执行对象 的接口信息,底层是通过接口来完成调用
Class<?>[] interfaces = target_vehicle.getClass().getInterfaces();
//创建InvocationHandler 对象
//因为 InvocationHandler 是接口,所以我们可以通过匿名对象的方式来创建该对象
/**
*
* public interface InvocationHandler {
* public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
* throws Throwable;
* }
* invoke 方法是将来执行我们的target_vehicle的方法时,会调用到
*
*/
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* invoke 方法是将来执行我们的target_vehicle的方法时,会调用到
* @param o 表示代理对象
* @param method 就是通过代理对象调用方法时,的哪个方法 代理对象.run()
* @param args : 表示调用 代理对象.run(xx) 传入的参数
* @return 表示 代理对象.run(xx) 执行后的结果.
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了....");
//这里是我们的反射基础 => OOP
//method 是?: public abstract void com.hspedu.spring.proxy2.Vehicle.run()
//target_vehicle 是? Ship对象
//args 是null
//这里通过反射+动态绑定机制,就会执行到被代理对象的方法
//执行完毕就返回
Object result = method.invoke(target_vehicle, args);
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了....");
return result;
}
};
/*
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
老师解读
1. Proxy.newProxyInstance() 可以返回一个代理对象
2. ClassLoader loader: 类的加载器.
3. Class<?>[] interfaces 就是将来要代理的对象的接口信息
4. InvocationHandler h 调用处理器/对象 有一个非常重要的方法invoke
*/
Vehicle proxy =
(Vehicle)Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}@Test
public void proxyRun() {
//创建Ship对象
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
//创建VehicleProxyProvider对象, 并且我们传入的要代理的对象
VehicleProxyProvider vehicleProxyProvider =
new VehicleProxyProvider(vehicle);
//获取代理对象, 该对象可以代理执行方法
//老师解读
//1. porxy 编译类型 Vehicle
//2. 运行类型 是代理类型 class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9
Vehicle proxy = vehicleProxyProvider.getProxy();
System.out.println("proxy的编译类型是 Vehicle");
System.out.println("proxy的运行类型是 " + proxy.getClass());
//下面老韩就要给大家解读/debug怎么 执行到 代理对象的 public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] args)
//梳理完毕. proxy的编译类型是 Vehicle, 运行类型是 class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9
//所以当执行run方法时,会执行到 代理对象的invoke
//如何体现动态 [1. 被代理的对象 2. 方法]
//proxy.run();
String result = proxy.fly(10000);
System.out.println("result=" + result);
}动态代理的动态怎么体现
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里可以切换 Vehicle 的 实现类(对象)
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
VehicleProxyProvider vehicleProxyProvider =
new VehicleProxyProvider(vehicle);
//给学员看一下 proxy 的结构. Vehicle proxy = vehicleProxyProvider.getProxy();
System.out.println("proxy 编译类型是 Vehicle");
System.out.println("proxy 运行类型" + proxy.getClass());
//动态代理的 动态怎么体现
//老韩认为
//1. proxy 运行类型是 com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 该类型被转型成Vehicle
// 因此可以调用 Vehicle 的接口方法
//2. 当执行 run() 的时候会调用, 根据 Java 的动态绑定机制, 这时直接调用Car的 run(),而是 proxy 对象的 invocationHandler 的 invoke 方法(!!!!!!)
//3. invoke 方法使用反射机制来调用 run()方法注意这个run 方法也可以是Vehicle 的其它方法)
// 这时就可以在调用 run()方法前,进行前置处理和后置处理//4. 也就是说 proxy 的 target_vehicle 运行类型只要是实现了Vehicle接口// ,就可以去调用不同的方法, 是动态的,变化的,底层就是使用反射完成的. proxy.run();
}
}AOP 的基本介绍
AOP 的全称(aspect oriented programming) ,面向切面编程
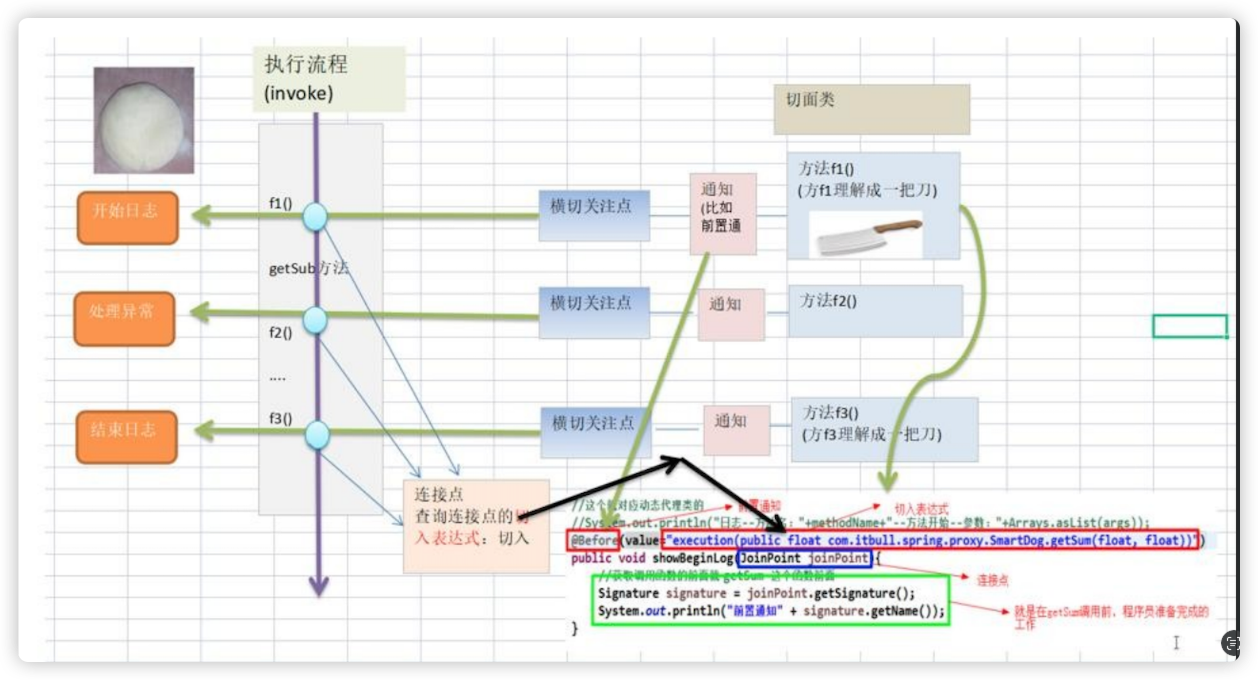
AOP 实现方式
基于动态代理的方式[内置 aop 实现]
使用框架 aspectj
AOP 编程快速入门
需要引入核心的 aspect 包
在切面类中声明通知方法
前置通知:@Before2)
返回通知:@AfterReturning
异常通知:@AfterThrowing
后置通知:@After
环绕通知:@Around
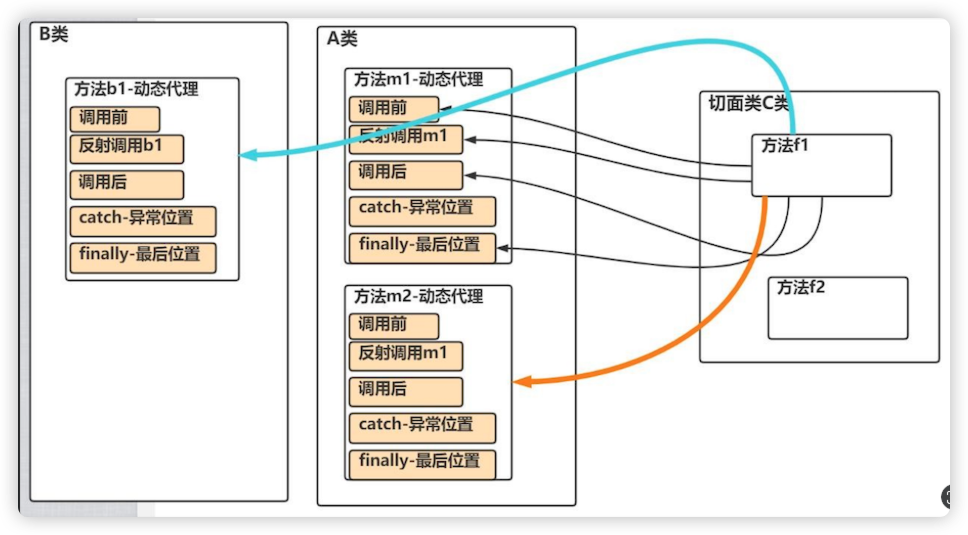
五种通知和前面写的动态代理类方法的对应关系

快速入门实例
. 导入 AOP 编程需要的包
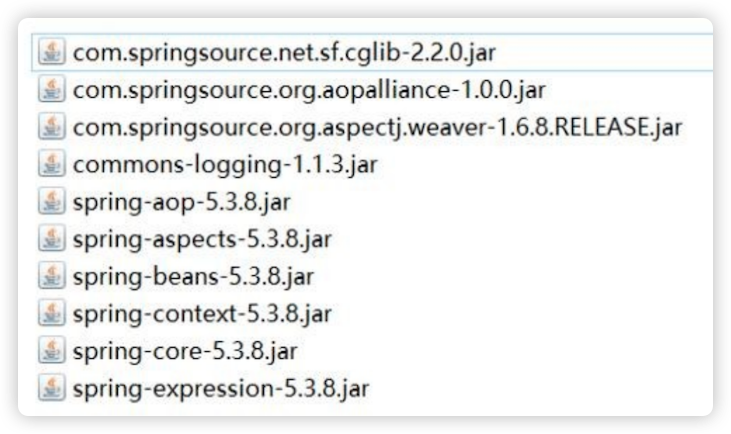
public interface SmartAnimalable {
//求和
float getSum(float i, float j);
//求差
float getSub(float i, float j);
}@Component //使用@Component 当spring容器启动时,将 SmartDog注入到容器
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable {
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float result = i + j;
//result = 1 / 0; //模拟一个算术异常
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
}
}/**
* 切面类 , 类似于我们以前自己写的MyProxyProvider,但是功能强大很多
*/
@Order(value = 2)//表示该切面类执行的顺序, value的值越小, 优先级越高
@Aspect //表示是一个切面类[底层切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定...)]
@Component //会注入SmartAnimalAspect到容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
//定义一个切入点, 在后面使用时可以直接引用, 提高了复用性
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)))")
public void myPointCut() {
}
//希望将f1方法切入到SmartDog-getSum前执行-前置通知
/**
* 老师解读
* 1. @Before 表示前置通知:即在我们的目标对象执行方法前执行
* 2. value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)
* 指定切入到哪个类的哪个方法 形式是: 访问修饰符 返回类型 全类名.方法名(形参列表)
* 3. showBeginLog方法可以理解成就是一个切入方法, 这个方法名是可以程序员指定 比如:showBeginLog
* 4. JoinPoint joinPoint 在底层执行时,由AspectJ切面框架, 会给该切入方法传入 joinPoint对象
* , 通过该方法,程序员可以获取到 相关信息
*
* @param joinPoint
*/
//@Before(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
//这里我们使用定义好的切入点
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 可以获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showBeginLog()[使用的myPointCut()]-方法执行前-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "-参数 "
+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
//返回通知:即把showSuccessEndLog方法切入到目标对象方法正常执行完毕后的地方
//老韩解读
//1. 如果我们希望把目标方法执行的结果,返回给切入方法
//2. 可以再 @AfterReturning 增加属性 , 比如 returning = "res"
//3. 同时在切入方法增加 Object res
//4. 注意: returning = "res" 和 Object res 的 res名字一致
//@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))", returning = "res")
//使用切入点
@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()", returning = "res")
public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showSuccessEndLog()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 返回的结果是=" + res);
}
//异常通知:即把showExceptionLog方法切入到目标对象方法执行发生异常的的catch{}
//@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))", throwing = "throwable")
//直接使用切入点表达式
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()", throwing = "throwable")
public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showExceptionLog()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 异常信息=" + throwable);
}
//最终通知:即把showFinallyEndLog方法切入到目标方法执行后(不管是否发生异常,都要执行 finally{})
//@After(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
//直接使用切入点
@After(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showFinallyEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showFinallyEndLog()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
//新的前置通知
//@Before(value = "execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.Phone.work()) || execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.Camera.work())")
//public void hi(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
// System.out.println("切面类的hi()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
//}
//切入表达式也可以指向接口的方法, 这时切入表达式会对实现了接口的类/对象生效
//比如下面我们是对UsbInterface 切入,那么对实现类Phone 和 Camera对象都作用了
@Before(value = "execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.UsbInterface.work())")
public void hi(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的hi()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
//给Car配置一个前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(public void Car.run())")
public void ok1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的ok1()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
//返回通知
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public void Car.run())")
public void ok2(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的ok2()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public void Car.run())")
public void ok3(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的ok3()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
//后置通知
@After(value = "execution(public void Car.run())")
public void ok4(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的ok4()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
//演示一下JoinPoint常用的方法.
joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); // 获取目标方法名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName(); // 获取目标方法所属类的简单类名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(); // 获取目标方法所属类的类名
joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers(); // 获取目标方法声明类型(public、private、protected)
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 获取传入目标方法的参数,返回一个数组
joinPoint.getTarget(); // 获取被代理的对象
joinPoint.getThis(); // 获取代理对象自己
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫描的包,根据实际情况配置即可 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj"/>
<!-- 开启基于注解的 AOP 功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>@Test
public void smartDogTestByProxy() {
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans08.xml");
//这里我们需要通过接口类型来获取到注入的SmartDog对象-就是代理对象
SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable =
ioc.getBean(SmartAnimalable.class);
//SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable =
// (SmartAnimalable)ioc.getBean("smartDog");
smartAnimalable.getSum(10, 2);
//System.out.println("smartAnimalable运行类型="
// + smartAnimalable.getClass());
System.out.println("=============================");
//smartAnimalable.getSub(100, 20);
细节说明
关于切面类方法命名可以自己规范一下, 比如 showBeginLog() . showSuccessEndLog()showExceptionLog(), showFinallyEndLog()
切入表达式的更多配置,比如使用模糊配置 @Before(value="execution(* com.hspedu.aop.proxy.SmartDog.*(..))")
表示所有访问权限,所有包的下所有有类的所方法,都会被执行该前置通知方法@Before(value="execution(* *.*(..))")当 spring 容器开启了
<!-- 开启基于注解的 AOP 功能 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>, 我们获取注入的对象, 需要以接口的类型来获取, 因为你注入的对象.getClass() 已经是代理类型了!当 spring 容器开启了
<!-- 开启基于注解的 AOP 功能 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>, 我们获取注入的对象, 也可以通过 id 来获取, 但是也要转成接口类型.
AOP-切入表达式
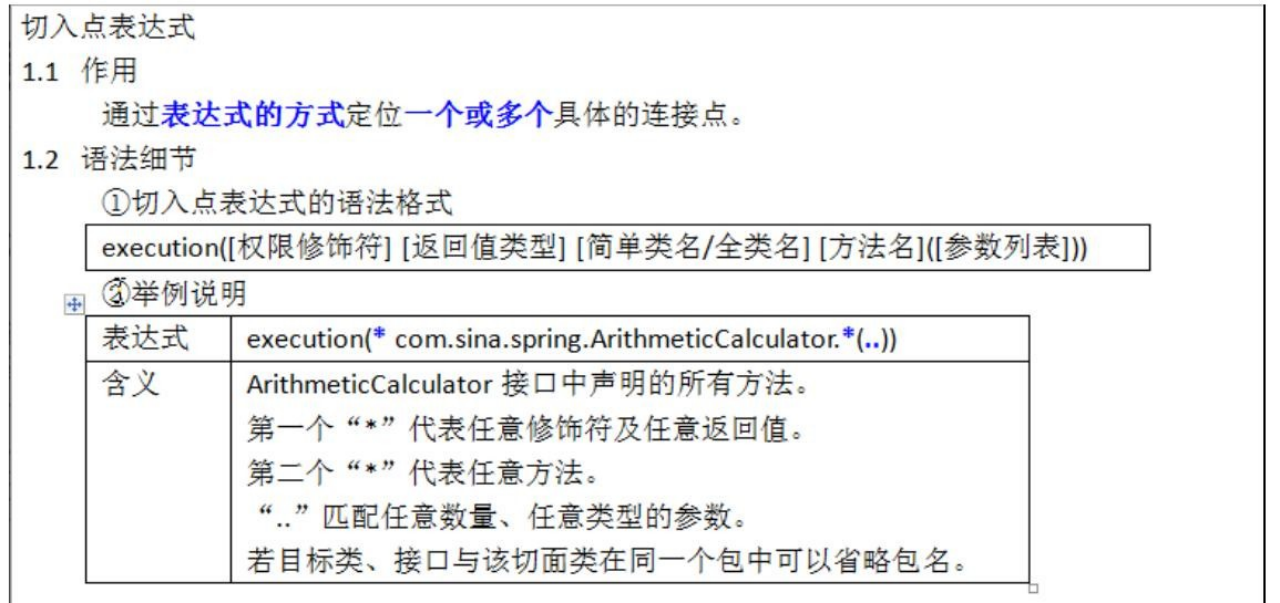
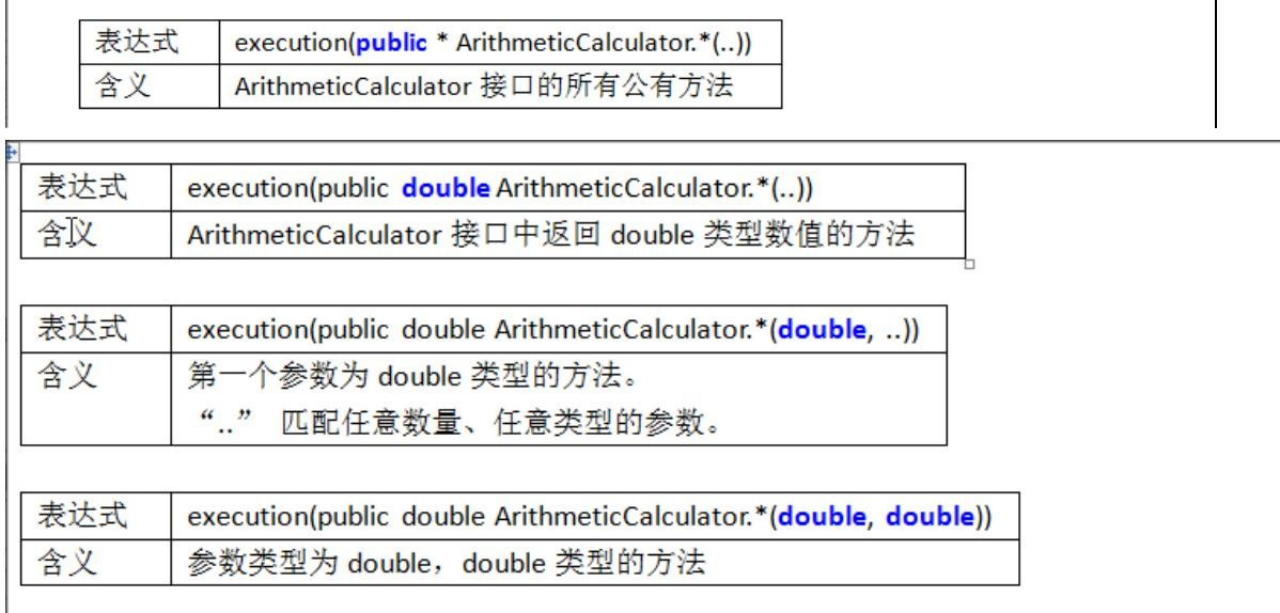
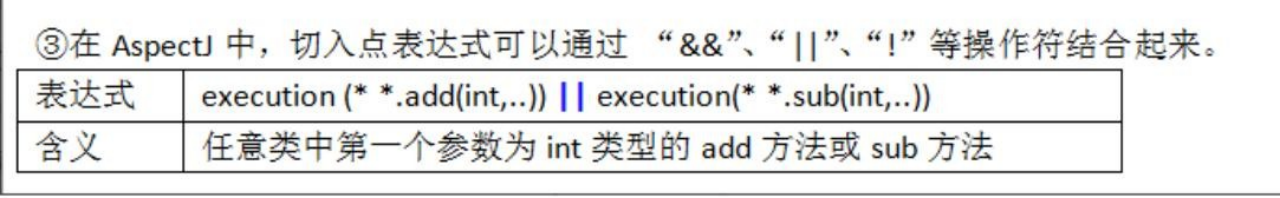
注意事项和细节
- 切入表达式也可以指向类的方法, 这时切入表达式会对该类/对象生效
- 切入表达式也可以指向接口的方法, 这时切入表达式会对实现了接口的类/对象生效
- 切入表达式也可以对没有实现接口的类,进行切入
动态代理 jdk 的 Proxy 与 Spring 的 CGlib
AOP-JoinPoint
通过 JoinPoint 可以获取到调用方法的签名
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); // 获取目标方法名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName(); // 获取目标方法所属类的简单类名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(); // 获取目标方法所属类的类名joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers(); // 获取目标方法声明类型(public、private、protected)
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); // 获取传入目标方法的参数,返回一个数组joinPoint.getTarget(); // 获取被代理的对象
joinPoint.getThis(); // 获取代理对象自己
}应用实例
如何在返回通知方法获取返回结果
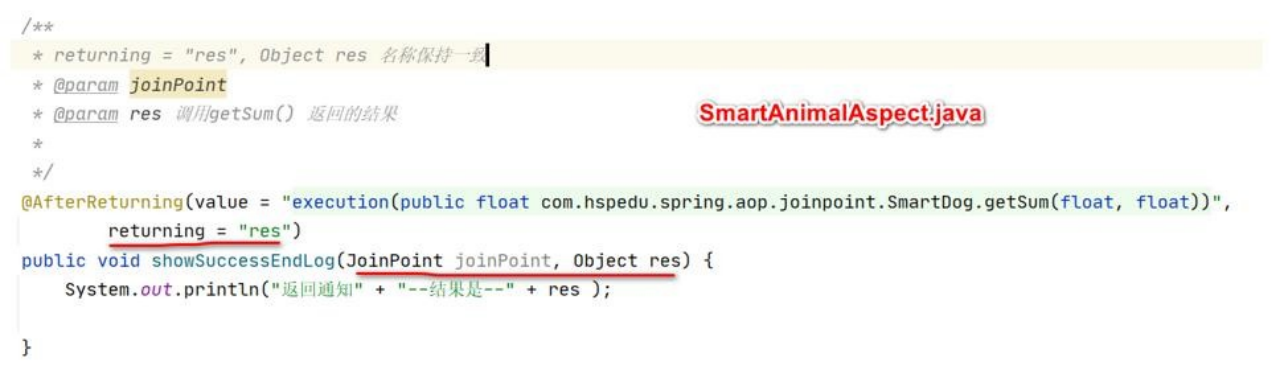
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))",returning = "res")
public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
System.out.println("返回通知" + "--结果是--" + res );
}AOP-异常通知中获取异常
如何在异常通知方法中获取异常信息。
//这个就对应动态代理类的
//System.out.println(" 日 志 -- 方 法 名 : "+methodName+"-- 方法抛出异常-- 异常类型:"+e.getClass().getName());
// @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float ,float))")
// public void showExceptionLog() {
// System.out.println("异常通知");
// }
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))", throwing = "throwable")
public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("异常通知 -- 异常信息--" + throwable);
}AOP-环绕通知【了解】
环绕通知可以完成其它四个通知要做的事情
/演示环绕通知的使用-了解
//老师解读
//1. @Around: 表示这是一个环绕通知[完成其它四个通知的功能]
//2. value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)) 切入点表达式
//3. doAround 表示要切入的方法 - 调用结构 try-catch-finally
@Around(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object result = null;
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
try {
//1.相当于前置通知完成的事情
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
List<Object> argList = Arrays.asList(args);
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-前置通知]" + methodName + "方法开始了--参数有:" + argList);
//在环绕通知中一定要调用joinPoint.proceed()来执行目标方法
result = joinPoint.proceed();
//2.相当于返回通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-返回通知]" + methodName + "方法结束了--结果是:" + result);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
//3.相当于异常通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-异常通知]" + methodName + "方法抛异常了--异常对象:" + throwable);
} finally {
//4.相当于最终通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-后置通知]" + methodName + "方法最终结束了...");
}
return result;
}环绕通知和动态代理完成的事情相似
AOP-切入点表达式重用
为了统一管理切入点表达式,可以使用切入点表达式重用技术
/*
* 这样定义的一个切入点表达式,就可以在其它地方直接使用*/
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void myPointCut() {
}
// @Before(value="execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) { //前置方法//得到方法的签名
// 调 用 前 置 通 知 对 应 的 方 法签名:float
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
//得到方法名. String method_name = signature.getName();
//得到参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
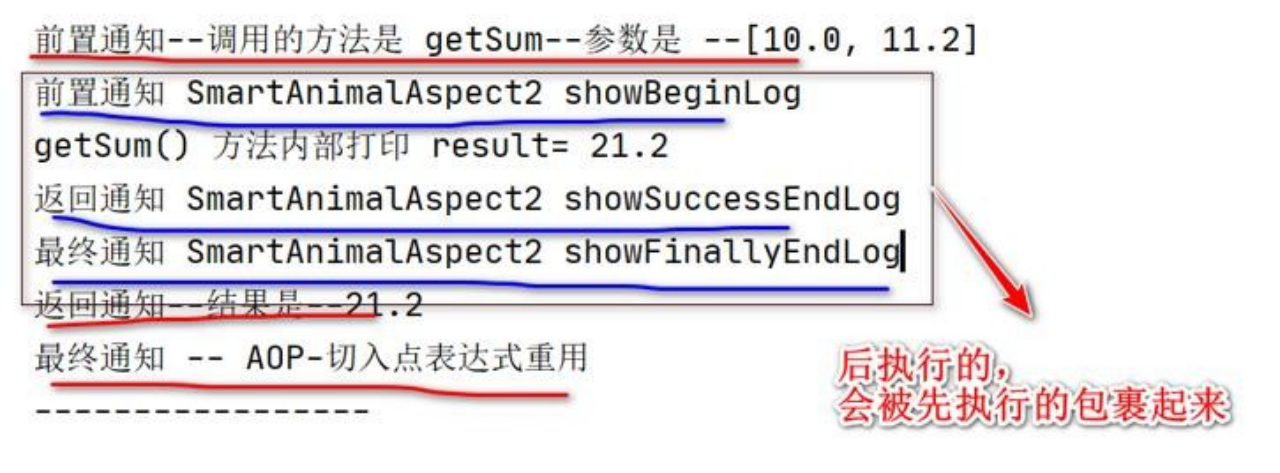
System.out.println("前置通知" + "--调用的方法是 " + method_name +"--参数是--" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
//@After(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
@After(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showFinallyEndLog() {
System.out.println("最终通知 -- AOP-切入点表达式重用");
}AOP-切面优先级问题
如果同一个方法,有多个切面在同一个切入点切入,那么执行的优先级如何控制.
基本语法
@order(value=n) 来控制 n 值越小,优先级越高.
@Aspect //表示这个类是一个切面类
@Order(value = 2)
@Component //需要加入 IOC 容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect2 {
/*
* 这样定义的一个切入点表达式,就可以在其它地方直接使用*/
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.joinpoint.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public void myPointCut() {
}
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("前置通知 SmartAnimalAspect2 showBeginLog");
}
}@Aspect
@Order(value = 1)
@Component
public class SmartAnimalAspect{
}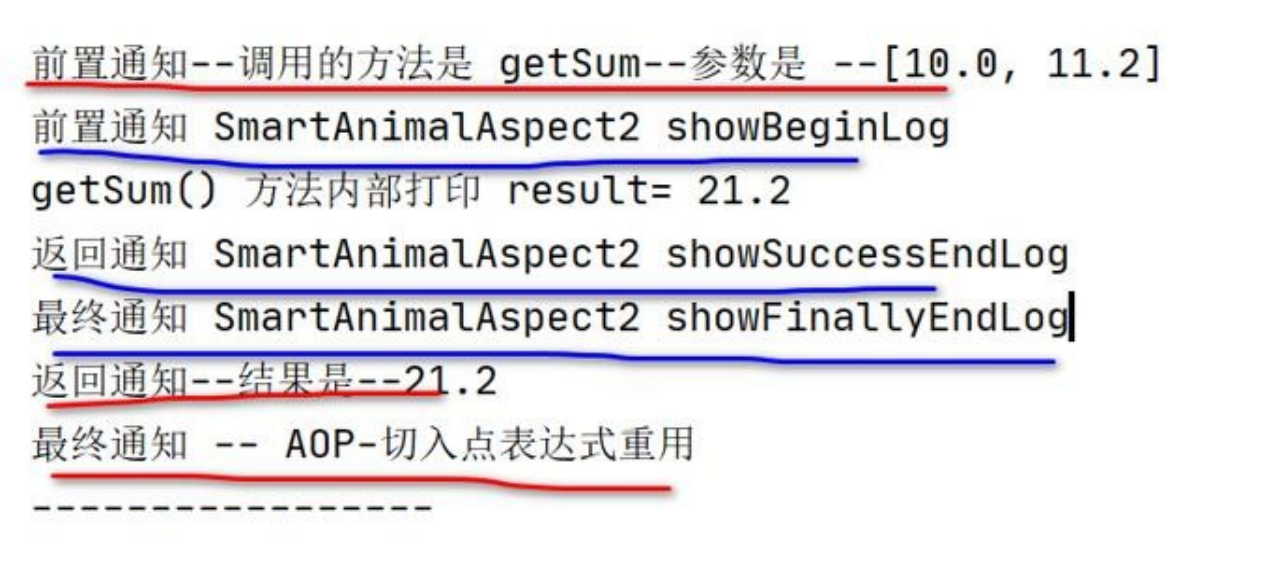
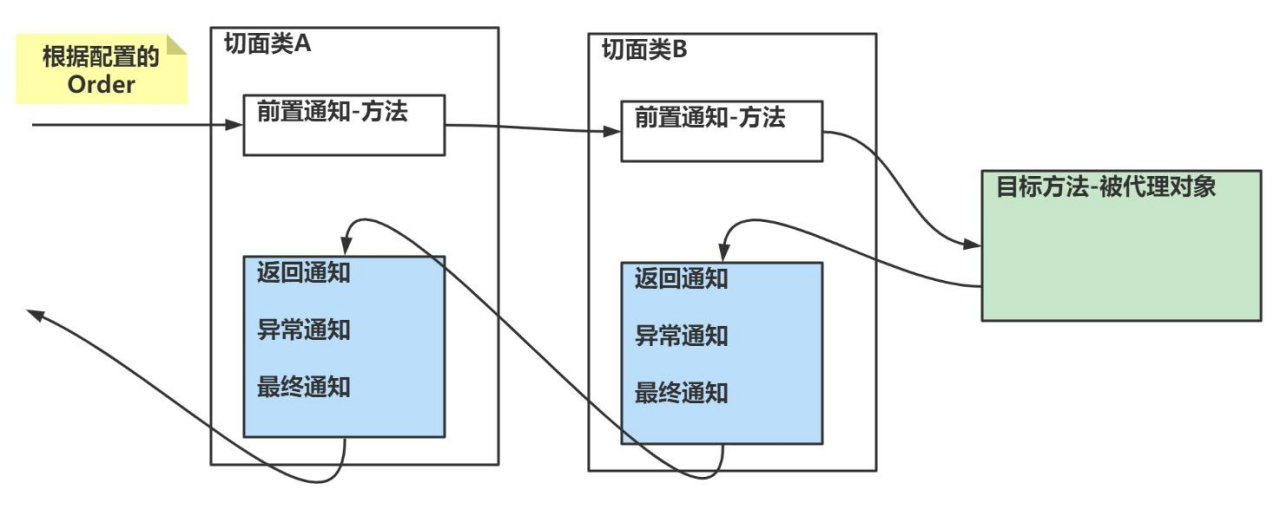
如何理解输出的信息顺序,类似 Filter 的过滤链式调用机制. (示意图-就比较清楚了.)
注意事项和细节说明
不能理解成:优先级高的每个消息通知都先执行,这个和方法调用机制(和Filter 过滤器链式调用类似)
AOP-基于 XML 配置 AOP
前面我们是通过注解来配置 aop 的,在 spring 中,我们也可以通过xml 的方式来配置AOP
public interface SmartAnimalable {
//求和
float getSum(float i, float j);
//求差
float getSub(float i, float j);
}//@Component //使用@Component 当spring容器启动时,将 SmartDog注入到容器
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable {
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float result = i + j;
//result = 1 / 0; //模拟一个算术异常
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
}
}/**
* 这是我们开发一个切面类, 但是不用注解,而是使用XML配置
*/
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 可以获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showBeginLog()[使用的myPointCut()]-方法执行前-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "-参数 "
+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showSuccessEndLog()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 返回的结果是=" + res);
}
public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showExceptionLog()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 异常信息=" + throwable);
}
public void showFinallyEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showFinallyEndLog()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 配置自动扫描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml"/>
<!-- 开启基于注解的 AOP 功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- 配置 SmartAnimalAspect bean -->
<bean id="smartAnimalAspect"class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartAnimalAspect"/>
<!--配置 SmartDog-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartDog"/>
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置统一切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public floatcom.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))"
id="myPointCut"/>
<aop:aspect ref="smartAnimalAspect" order="1">
<!-- 配置各个通知对应的切入点 -->
<aop:before method="showBeginLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/><aop:after-returning method="showSuccessEndLog"pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="res"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="showExceptionLog"pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="throwable"/>
<aop:after method="showFinallyEndLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/><!-- 还可以配置环绕通知 -->
<!-- <aop:around method=""/> -->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans> Blog
Blog